Engaging Young Minds: A Systematic Literature Review on the Role of Blended Learning Models in Primary Education
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijste.5.1.1436bKeywords:
Blended learning, roles, primary education, reviewAbstract
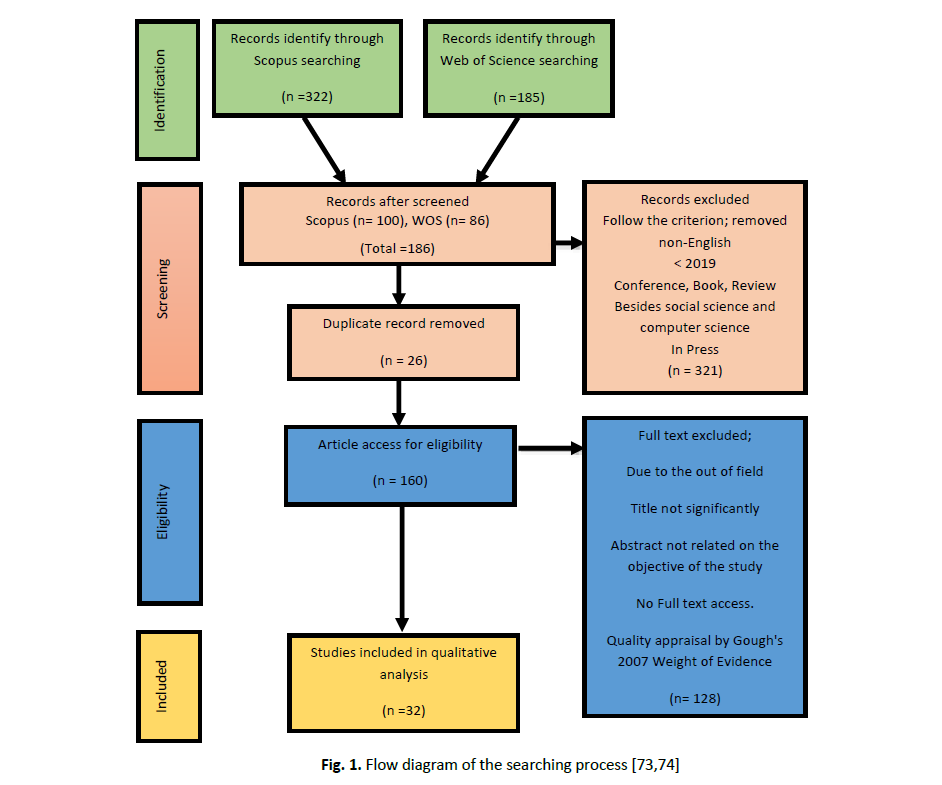
The integration of blended learning models in primary education has gained increasing attention due to their potential to enhance pupil engagement and learning effectiveness especially after pandemic COVID 19. This systematic literature review aims to synthesize existing research on the role of blended learning in fostering young learners' participation, academic development, and instructional adaptability. The problem addressed in this study is the need for a comprehensive understanding of how blended learning models impact primary education and the challenges associated with their implementation. The methodology involved a rigorous search and analysis of indexed and peer-reviewed articles from reputable databases such as Scopus and Web of Science, published between 2019 and 2024. The study followed the PRISMA framework to ensure a systematic selection and review process. A total of (n=32) studies met the predefined inclusion criteria, focusing on various blended learning approaches, including flipped classrooms, station rotation, and hybrid models. The findings were categorized into four main themes (1) Blended Learning and Language Acquisition (2) Blended Learning in STEM and Science Education, (3) Pupil Engagement, Motivation, and Inclusivity (4) COVID-19 and Post-Pandemic Education. Results indicate that blended learning highlight its effectiveness in improving reading comprehension, language proficiency, and STEM achievement, especially for pupils from low-income backgrounds. Integration of Augmented Reality and gamification into blended learning further enhance learning experiences. This review provides valuable insights for future research in explore long-term impacts, adaptive learning technologies, and digital equity in blended learning, especially for underprivileged communities.