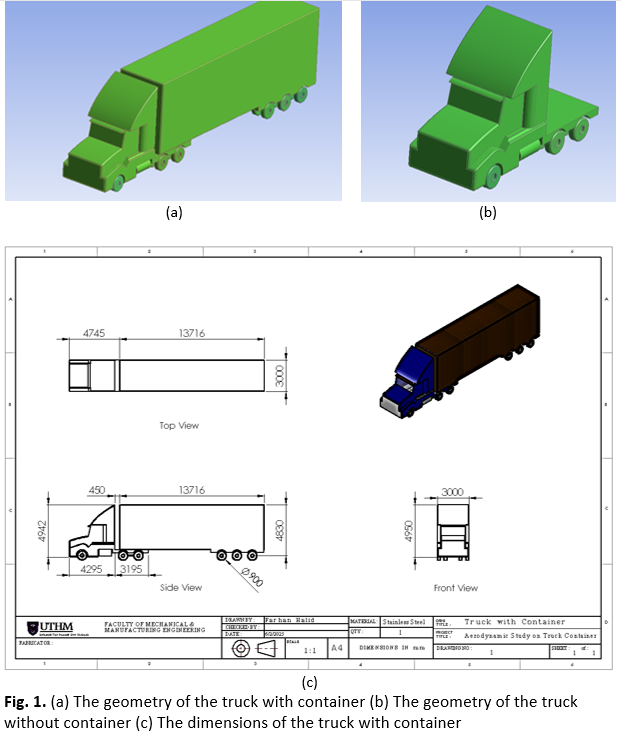
Aerodynamic Performance Analysis of a Truck under Varying Wind Velocities and Container Configurations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sjotfe.5.1.2135aKeywords:
K-omega SST, k-Epsilon, truck, drag coefficient, ANSYS Fluent, lift coefficient, turbulence modelsAbstract
This study explores the aerodynamic performance of a container truck by analyzing the flow characteristics, drag, and friction coefficients using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). Various wind velocities (20 m/s, 25 m/s, and 30 m/s) and turbulence models, including k-Epsilon, k-omega SST, Transition SST, and k-kl-omega, were evaluated to understand their effects on aerodynamic behavior. The results indicate that the k-omega SST and Transition SST models provide more accurate predictions of real-world aerodynamic behavior, particularly in capturing flow separation and wake structures. The pressure distribution analysis reveals high-pressure zones at the front of the container and low-pressure wake regions behind it, contributing to increased drag. The drag coefficient for the truck without a container ranged from 4,118 to 9,423, while for the truck with a container, it varied from 4,459 to 9,994 across different turbulence models. Velocity contours show significant turbulence in the wake region, increasing with wind speed. Lift coefficients varied significantly, with the k-Epsilon model consistently predicting downward forces, enhancing stability. Overall, the study highlights the importance of turbulence model selection and provides insights into optimizing truck aerodynamics for up to a 15% reduction in drag, which directly impacts fuel efficiency.