Thermal and Electrical Properties of Zinc-Strontium-Lithium Phosphate Glass Doped with Carboxymethyl Cellulose
Keywords:
Phosphate glass, DTA, EISAbstract
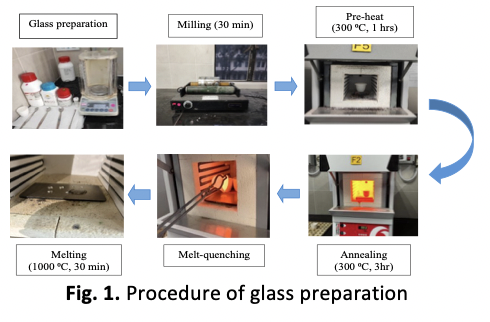
The influence of Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) on the thermal and electrical properties of phosphate glass has attracted considerable attention, yet its mechanistic role in modifying glass structure remains insufficiently understood. This study aims to synthesize and characterize phosphate glasses with composition (40−x)P₂O₅–30ZnO–25Li₂O–5SrO–(x)CH₂COOH (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5 mol%) to elucidate how CMC incorporation reshapes the glass network and alters its physical, thermal, and electrical behavior. The glasses were prepared by melt-quenching and characterized using XRD, DTA, and EIS analyses. Density increased from 2.604 to 3.194 g/cm³ and molar volume decreased to 29.326 cm³·mol⁻¹ at 0.2 mol% CMC, indicating stronger network compaction. The optimal composition at 0.2 mol% CMC exhibited the highest ionic conductivity (2.89 ×10⁻⁷ S·cm⁻¹) and lowest activation energy (1.20×10⁻² eV). This enhancement arises from CMC’s carboxylate groups, which form hydrogen-bonded linkages with phosphate tetrahedra and stabilize Li⁺ pathways within the matrix. The findings demonstrate that low-level CMC addition effectively tunes network rigidity, ionic mobility, and dielectric response, providing a green and sustainable strategy for tailoring the performance of phosphate-based functional glasses.