Development of Electronic Braille Notetaker Algorithms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijese.6.1.4855Keywords:
Braille, notetaker, visually impaired, raspberry pi, braille cell moduleAbstract
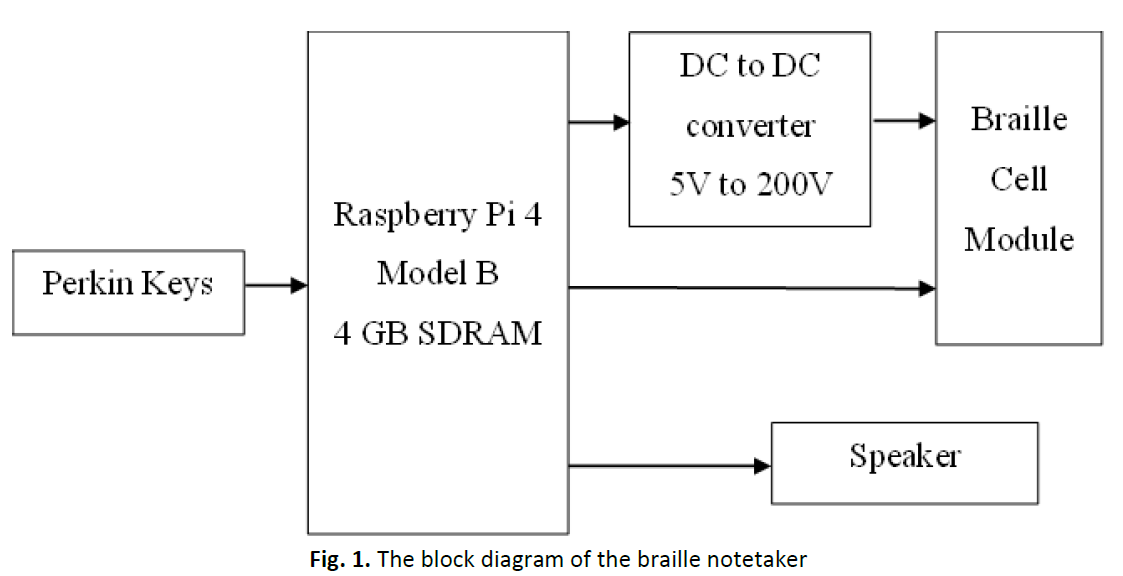
In this era of high technology, most of the blind and visually impaired people are still used to Braille encoding in reading or writing. Currently, they are still using a manual mechanical typewriter called Perkin Brailler to take down notes during lectures or meetings. However, this typewriter is expensive and difficult to carry around, also heavy and can be broken down easily. Furthermore, Perkins Brailler can only type the characters on the paper physically. It cannot save the document as a softcopy and also connect the link to a desktop or laptop. The objectives of this paper are to develop the algorithm of an electronic braille notetaker system that can perform the basic notetaker features as well as the translation between the braille code and text. The scope of this project limited the file type to text file format and only grade 1 (uncontracted) braille is used. The braille notetaker prototype is composed of Raspberry Pi 4, mechanical switches, DC to DC converter, and a speaker. The algorithm generated provides the braille notetaker several features which can be categorized into File Manager, Reading Mode, Editing Mode, Trash, Setting, and Searching Mode. The typing speed can reach 0.3233s per character or 3 characters per second and the accuracy can achieve 97.5%. Thus, this braille notetaker can help blind people perform similar tasks to other normal people without obstacles during their school life or working hours. Blind people can learn at school, work at any company, and have the same right and power in writing and reading as other normal people.