Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry in Monitoring Bridge Deformation Caused by Flood Event
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijcse.5.1.2433Keywords:
Differential interferometry, remote sensing, bridge assessment, vertical displacement, horizontal displacement, floodAbstract
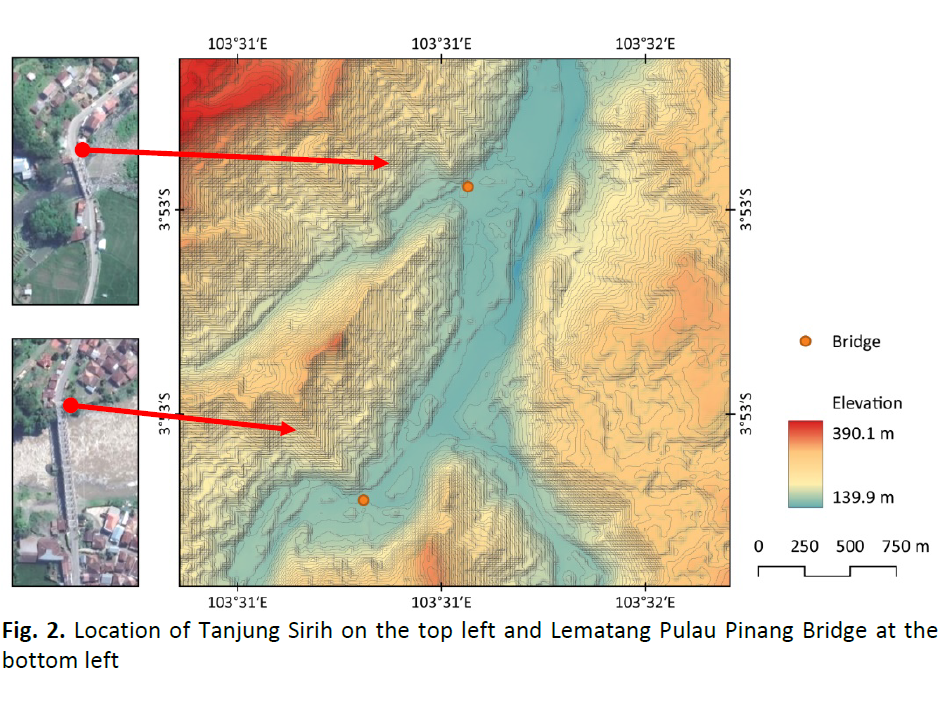
Many vital infrastructures, which are necessary for society and the economy to function, are heavily dependent in the modern world. Any interruption to such crucial processes can have adverse effects on society. Large transportation networks must be thoroughly inspected, which requires expensive infrastructure management costs. As a result, early signs of challenges can go unnoticed, which could result in disastrous structural failures. In order to evaluate structural safety over time, infrastructure assets must be monitored. Analysing the remote sensing radar data can identify deformation patterns and structural integrity that might endanger a bridge and its users. This study aims to examine the deformations of two bridges by comparing remote sensing measurements taken before and after a flood event, providing insights into temporal changes in bridge structural integrity. The study focused on assessing bridge deformations, encompassing both vertical and horizontal displacements, using radar remote sensing data with differential interferometry while minimising the decorrelation from low coherence of vegetated areas. From the result, the vertical and horizontal displacements were estimated at 30 mm to 40 mm after the flood. The data can be suitable to improve bridge design by exposing elements that cause bridge deformation over time and help assess the damage for priority repairs.