The Effect of Fly Ash and Alkali Activator Mass Ratio (FA/AA) and Curing Conditions on the Mechanical Properties of High Compressive Strength Geopolymer Mortar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijcse.5.1.110Keywords:
Fly ash, alkali activator, geopolymer, aluminosilicate, compressive strengthAbstract
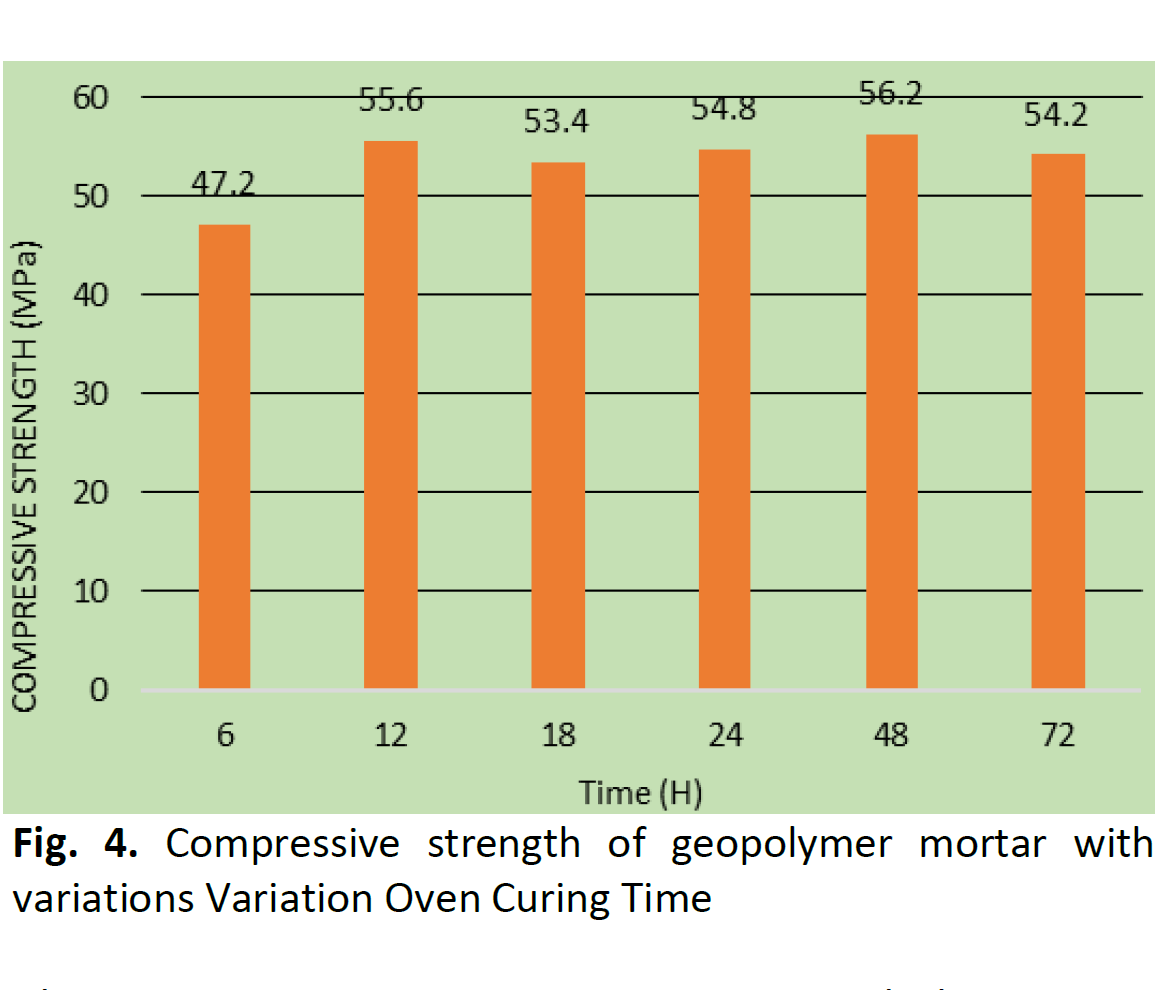
Cement production is not an environmentally friendly process, as it consumes a lot of energy. One of the cement production processes is the sintering of calcareous and clay materials which is responsible for CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Globally, Cement production is associated with excessive carbon dioxide emissions. Geopolymer is an environmentally friendly alternative to replace Portland cement. Geopolymer is synthesized by a chemical reaction (geopolymerization) between aluminosilicate materials (industrial by-products, such as blast furnace slag or fly ash) and alkali activators. Fly ash is an aluminosilicate material from coal combustion residue that can be used as a geopolymer material to make more environmentally friendly mortar. Geopolymer mortar with FA/AA variations with a FA/AA variation range of 1.75-3.25 has an optimal compressive strength, namely at a ratio of 2.75 with a value of 57.6 Mpa. Oven curing for 48 hours is the optimum value with a value of 56.2 MPa and the highest compressive strength value was obtained at curing at a temperature of 140℃, namely 55.2 MPa.