Psychological Determinants in Influencing Residents Adoption Intention of Home Energy Efficiency Measures: A Case in East Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijap.5.1.114bKeywords:
Energy efficiency measures, psychological determinants, intention, Theory of Planned BehaviorAbstract
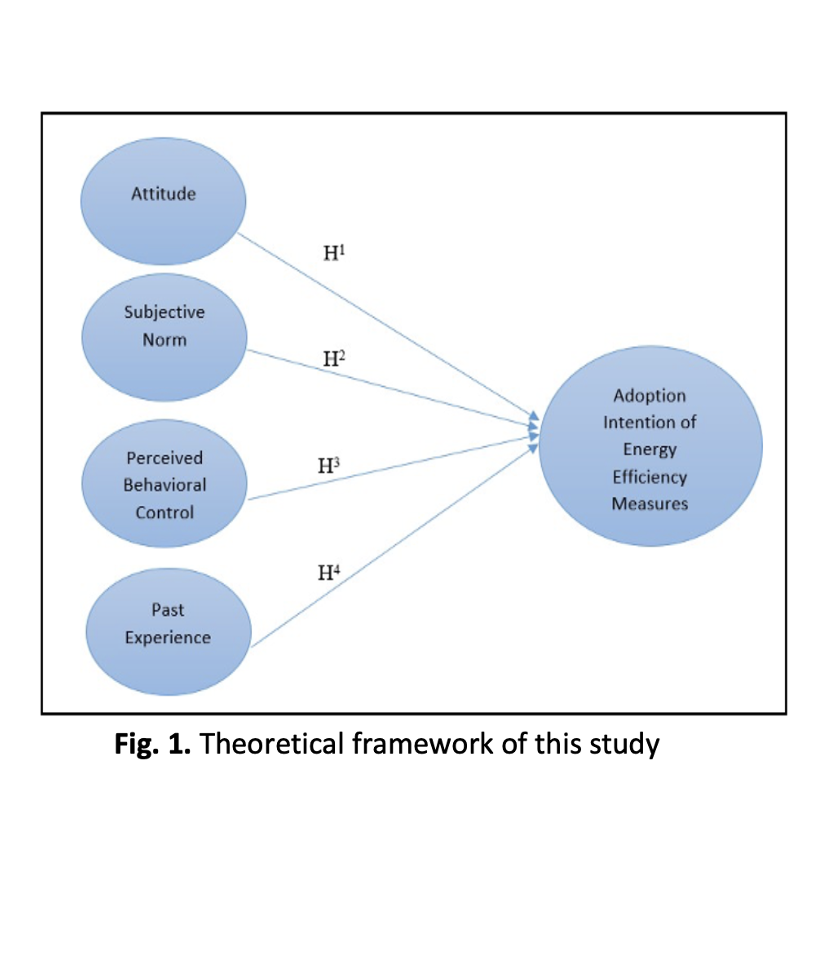
In recent years, energy demand has been growing fast, primarily driven by global population growth. The residential sector is a major contributor to rising energy needs, accounting for 20.5% of Malaysia’s energy consumption. A substantial portion of domestic energy is used for electrical appliances, water heating, cooling and lighting, all of which contribute to increased greenhouse gas emissions. To reduce energy demand, carbon emissions and energy costs at both household and national levels, energy efficiency measures can play a crucial role. However, the factors influencing the adoption of these measures remain unclear within the Malaysian context. This study aims to explore the significance of psychological determinants in influencing residents' intentions to adopt home energy efficiency measures. Grounded in the Theory of Planned Behavior, a theoretical framework was developed, incorporating an additional variable to assess its potential impact on residents' intentions to adopt home energy efficiency measures. A systematic literature review identified four key psychological determinants—attitude, subjective norm, perceived behavioral control and past experience—as influencers of residents’ intentions to adopt energy efficiency measures. A questionnaire survey was conducted among 286 residents in Sibu, Sarawak. Frequency analysis was used to examine demographic information, and Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) was employed to analyze relationships within the model. Findings revealed that all determinants, except subjective norm, significantly influence households’ intentions to adopt home energy efficiency measures. The results provide insights for marketers and policymakers to shape targeted strategies, fostering a more sustainable society.