Techno-Economic Assessment of Rooftop Solar PV Systems for Malang City Hall Using HOMER Pro
Keywords:
Rooftop solar PV, techno-economic analysis, HOMER Pro, net present cost, Malang CityAbstract
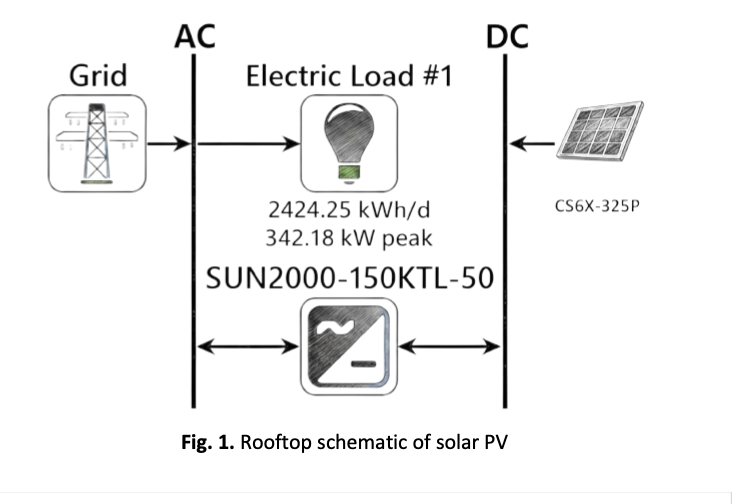
The urgent necessity for the use of renewable energy is highlighted by Indonesia's growing energy demand and dependence on fossil fuels. In line with the national renewable energy target of 23% by 2025, this study assesses the technological and financial viability of a rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) system at Malang City Hall. HOMER Pro was used to simulate and optimize the system using solar radiation data, load profiles, and local power rates. The best PV arrangement, according to the analysis, is 3.25 kW, which can reduce grid dependency while providing the majority of the building's electrical needs. The project's feasibility was validated by economic evaluation using Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE), and Net Present Cost (NPC), bolstered by sensitivity analysis on PV costs and financial parameters. The findings provide a reproducible model for government buildings throughout Indonesia and show that rooftop PV systems can provide long-term financial and environmental benefits.