Smart HVAC Filtration Monitoring for Indoor Air Quality (IAQ): Enhance Efficiency and Environmental Sustainability
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/scsl.3.1.114Keywords:
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ), air quality monitoring, HVAC system, air filters, real-time sensor, energy efficiency, sustainable filtrationAbstract
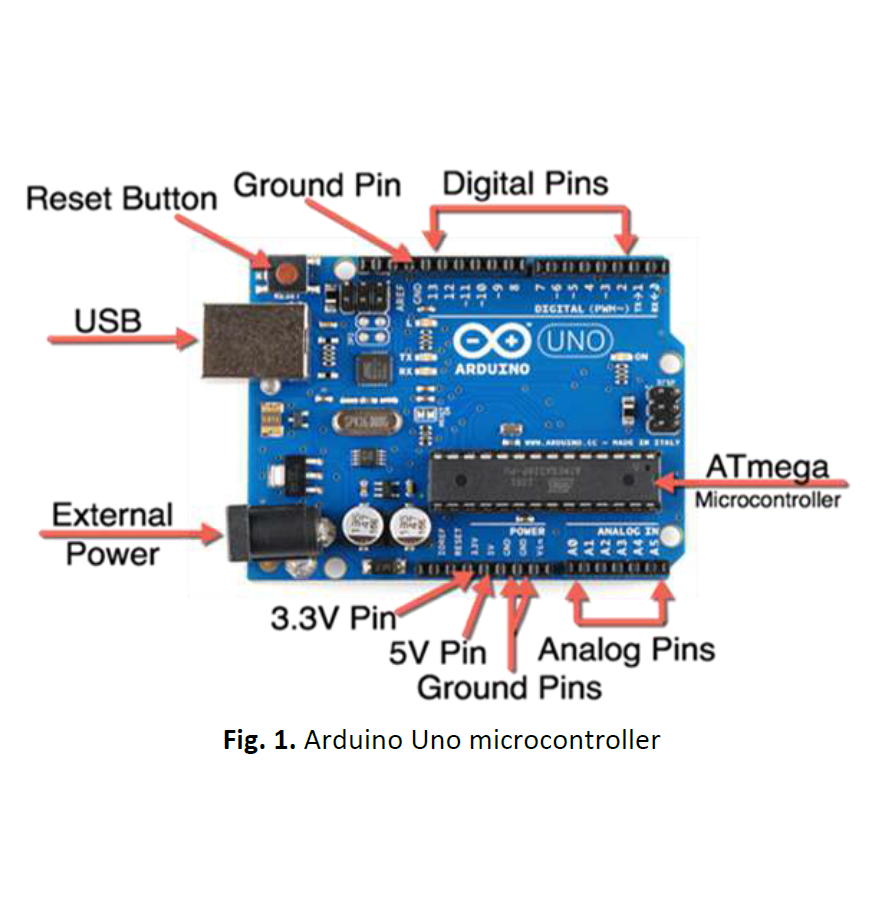
Air filters play a vital role in HVAC systems by preventing pollutants such as dust and smoke from circulating indoors. Poor air filtration negatively impacts Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) and increases energy consumption. This study aims to develop a real-time air quality monitoring system for ducted air conditioning systems, specifically in an Air Handling Unit (AHU), to enhance filtration efficiency and optimize HVAC performance while improving IAQ. The system integrates humidity, temperature, dust, and airflow sensors with an Arduino microcontroller to collect and display real-time data. Two sensors were placed at pre-filter and post-filter positions to measure airborne particle concentration before and after filtration. Experimental results show that Sensor 1 recorded higher dust levels, while Sensor 2 measured significantly lower values, confirming the air filter’s effectiveness. Clogged filters were found to reduce airflow by up to 50%, increasing energy consumption by 15–30%. The findings highlight the importance of real-time monitoring in improving IAQ, optimizing filter maintenance, and reducing energy waste. Implementing smart filtration monitoring systems can enhance HVAC efficiency, lower operational costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability.