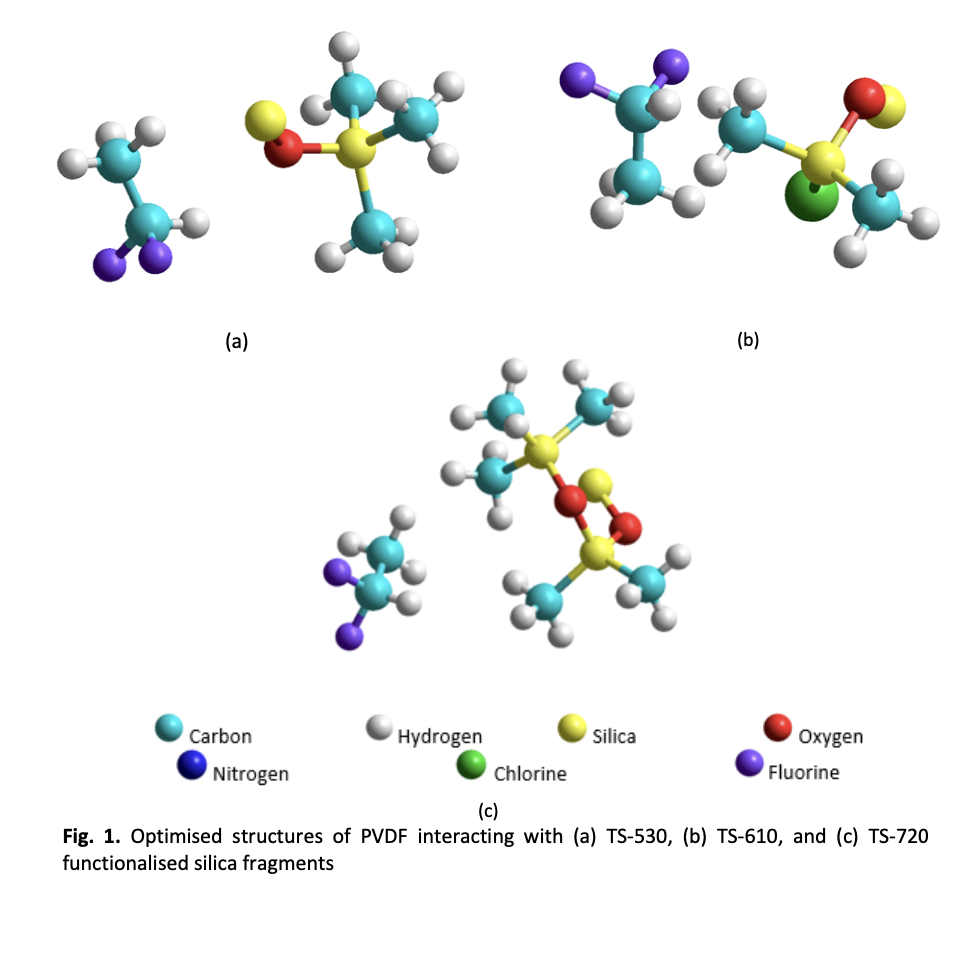
Molecular Insight into Functionalised Fumed Silica–PVDF Interactions: A Simulation-Based Approach for Understanding Filler–Polymer Compatibility in MMMs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijn.5.1.113Keywords:
Molecular simulation, polymer–filler compatibility, functionalised silica nanoparticles, mixed matrix membranesAbstract
Silica nanoparticles, one of the fillers that have been used in mixed matrix membranes, can be functionalised to increase its compatibility with polymer matrices of the membrane. However, the molecular interactions that govern this compatibility are often poorly understood and difficult to assess prior to fabrication. This work aims to assess the interaction strength between silica fillers that have been functionalised with three organosilicon dubbed TS-530, TS-610, and TS-720 and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane matrix using molecular simulation. It is desired to determine whether computation modelling can reliably predict filler-polymer compatibility by comparing with experimental observations. Therefore, geometry optimisations and binding energy calculations were done using MM+, AM1, and PM3 methods in HyperChem 8.0 software. Each silica surface was modelled as a functionalised silanol core that has been treated with HMDS, DMDCS, and PDMS, representing TS-530, TS-610, and TS-720 functionalised silica nanoparticles respectively, then paired with a PVDF oligomer as the membrane matrix. The simulation results showed that TS-530 exhibited the most favourable interaction with PVDF, with the strongest binding energy and the most consistent surface contact. On the other hand, TS-610 and TS-720 showed weaker and more localised interactions with PVDF. These results are consistent with the experimental results for the mixed matrix PVDF membranes with functionalised silica nanoparticles as fillers. TS-530 mixed matrix membranes showed more uniform nanoparticle dispersion, higher contact angle and LEPw values, signifying better membrane wetting resistance. Additionally, it showed superior CO2 permeability and selectivity compared to other mixed matrix membranes. This study demonstrates that it is possible to use molecular modelling to effectively predict polymer-filler compatibility in membrane materials. The ability to predict dispersion and interface behaviour from simulated interaction energies offers a valuable screening tool for selection of materials for membrane design.