Revolutionizing Grammar Mastery: Empowering Learners through Quizizz to Combat Social Media Language Challenges
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/spcse.1.1.3140aKeywords:
Multimodal, Quizizz, grammar proficiencyAbstract
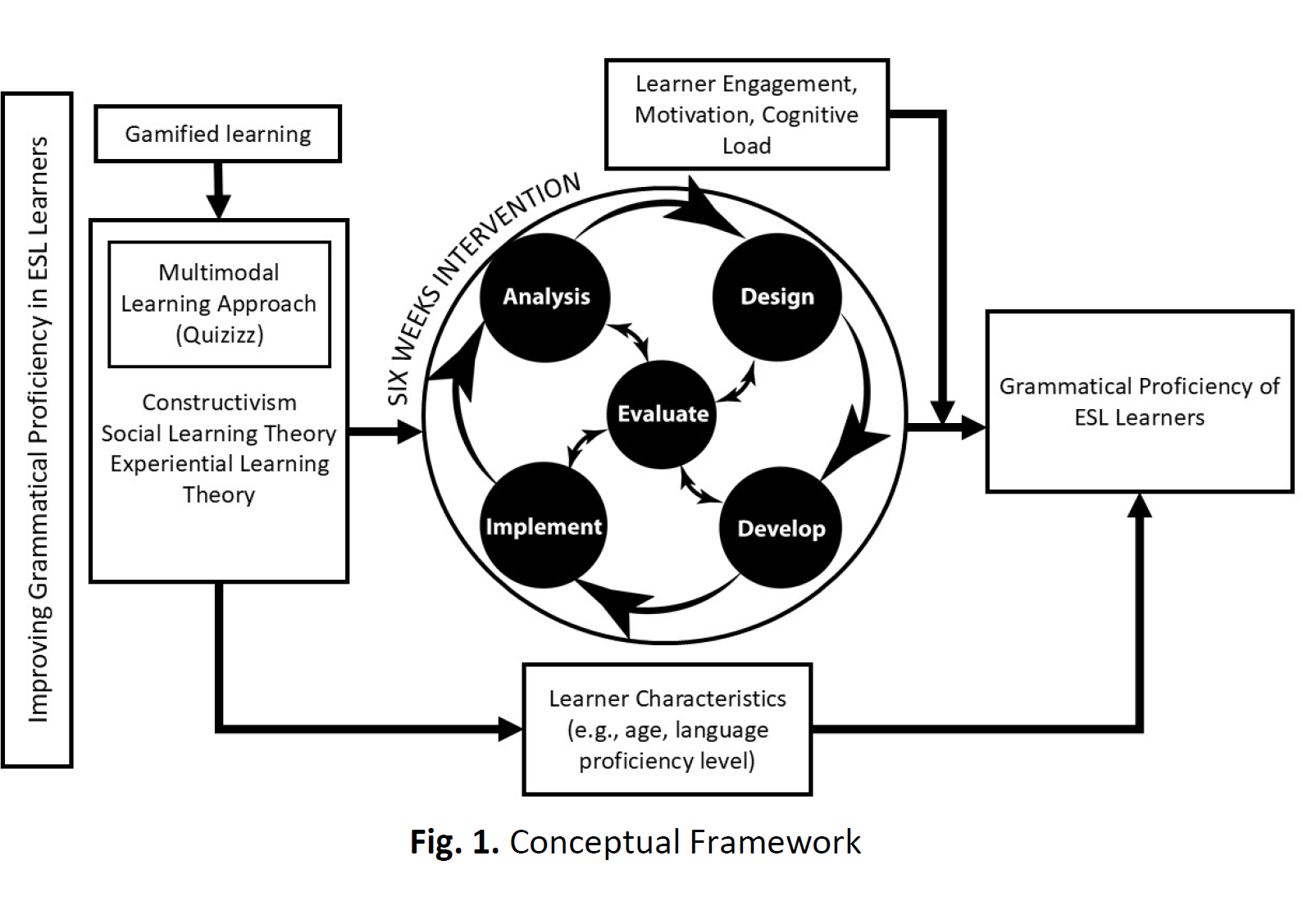
The proliferation of social media has dramatically transformed communication patterns, significantly impacting the language acquisition process among English as a Second Language (ESL) learners. With the increasing use of informal language—characterized by emojis, slang, colloquialisms, and abbreviations—students often struggle to adapt their writing and speaking skills to formal academic contexts. This study investigates the effectiveness of a 6-week multimodal approach that integrates Quizizz, a gamified online quiz platform, to improve grammar proficiency among Malaysian primary and secondary school students. Data were collected through pre- and post-tests, surveys, and semi-structured interviews involving 44 participants. The pre-test results indicated a mean score of 45.75 with a standard deviation of 15.763, reflecting a significant lack of understanding prior to the intervention. In contrast, the post-test results revealed a mean score of 93.18 and a lower standard deviation of 8.766, indicating substantial improvement and consistent performance among students after the intervention, with statistical analysis confirming significant increases (p < .001). Participants reported positive experiences with Quizizz, recognizing its effectiveness in bridging the gap between informal social media language and formal academic communication. Overall, this research underscores the importance of incorporating social media literacy into English education to equip students with the skills needed for effective communication in diverse contexts while leveraging informal language exposure as a learning tool.