Exploring Flow Stability: Influence of Slip, Soret, and Dufour on Cu-Water Nanofluid over a Stretching/Shrinking Sheet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/spaset.2.1.1531Keywords:
Stagnation point flow, nanofluids, stretching/shrinking, second-order slip, Soret and Dufour effects, stability solutionsAbstract
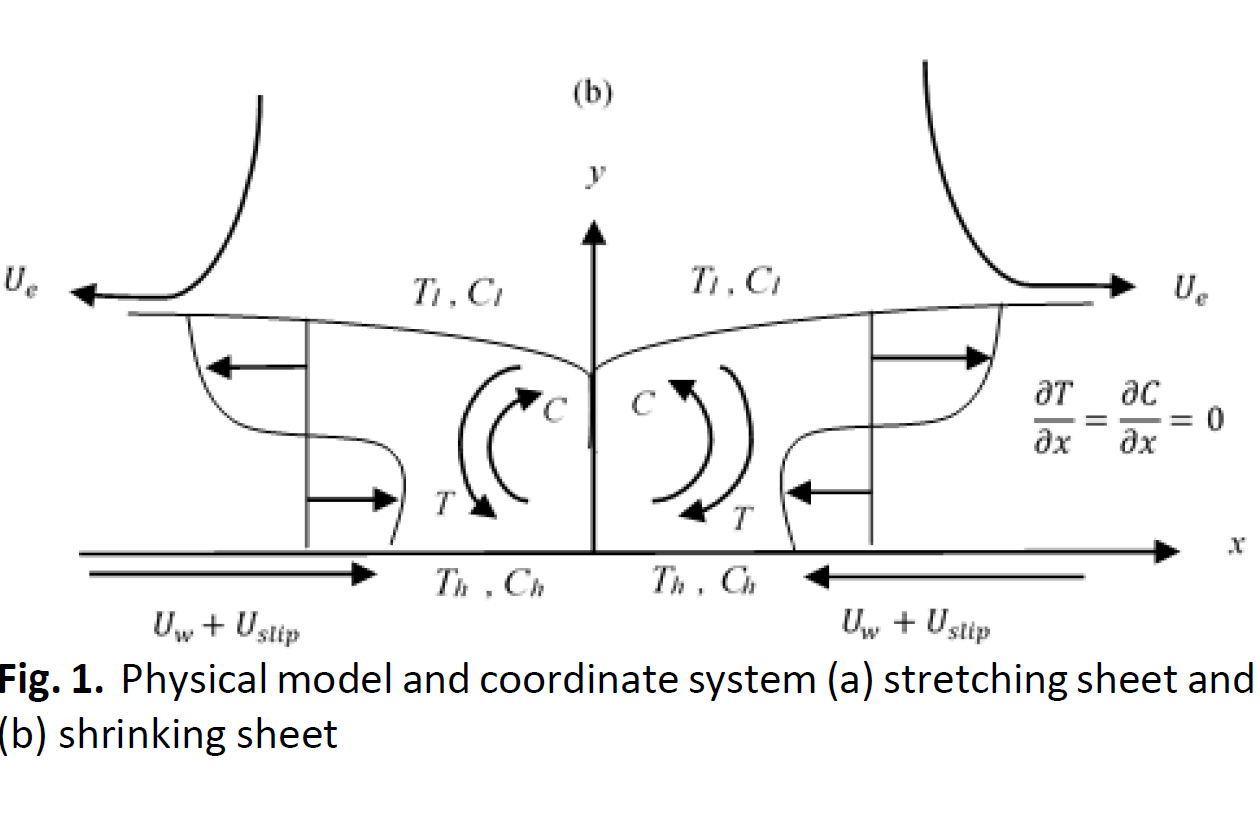
Nanofluids have gained significant attention in industrial and engineering applications due to their enhanced thermal conductivity, making them suitable for cooling systems, heat exchangers, and electronic devices. Despite extensive research on boundary layer flow in nanofluids, the influence of thermodiffusion (Soret effect) and diffusion-thermo (Dufour effect) in the presence of second-order slip has not been thoroughly explored. This study aims to investigate the effects of second-order slip, Soret, and Dufour parameters on stagnation boundary layer flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet immersed in a Cu-water nanofluid. The primary objective is to analyze how these parameters influence skin friction, heat transfer, and mass transfer characteristics. The governing partial differential equations are transformed into ordinary differential equations using similarity transformations and numerically solved via the bvp4c solver in MATLAB. Results indicate that the presence of the first-order slip parameter broadens the solution region, whereas the second-order slip parameter narrows it. Additionally, the Soret effect enhances the heat transfer rate, while the Dufour effect increases mass transfer at the surface. The study also reveals the existence of dual solutions, necessitating a stability analysis to determine which solution is physically realizable. The findings provide valuable insights into optimizing nanofluid applications in industrial and engineering processes.