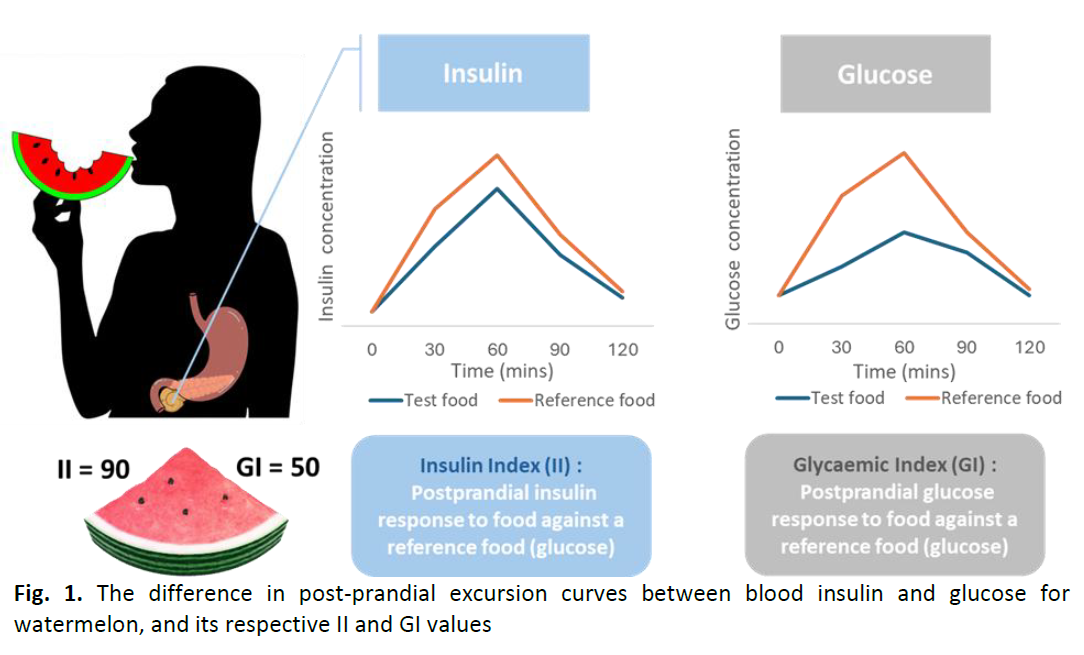
Insulin Index – A “Decretin” Approach in the Era of “Incretin”
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijphpc.5.1.3946Keywords:
Decretin, incretin, insulin index, insulinaemic index, entero-insular, GLP-1, hyperinsulinemiaAbstract
Obesity and diabetes have become prevalent health issues globally, with significant impacts on the Asian population, including Southeast Asia. This paper explores the concept of "decretin," which focuses on minimising insulin secretion through dietary strategies. This concept is in contrast to the incretin-based approaches that enhance insulin release. The Insulin Index (II), which measures the insulin response to various foods in comparison to a reference food, is proposed as a tool that may be manipulated for the preferred decretin action. Decretin involves dietary strategies to reduce insulin excursion, potentially offering therapeutic benefits for insulin resistance and diabetes. This paper emphasises the discussion of foods with low II values, insulin responses, and the strategies for insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. This may open further research pathways on the decretin action to develop tailored dietary guidelines for diabetes management in the Southeast Asian region.