Radiation Doses from Computed Tomography of The Brain Based on Head Sizes in A Diagnostic Center in Northern Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijphpc.4.1.5258Keywords:
CT brain, effective dose, effective diameter, radiation doseAbstract
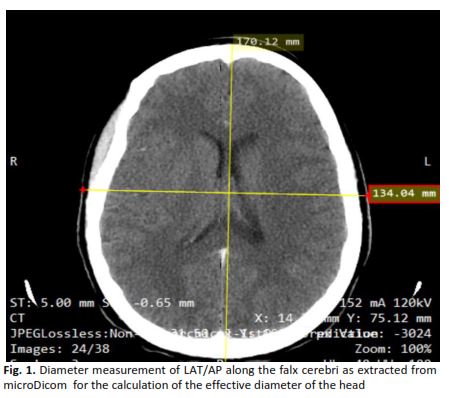
The study aims to evaluate and assess radiation dose and its relationship with the effective diameter of the head for CT brain examinations conducted using a 16 multi-slice CT scanning machine. Data from 30 patients who had CT brain examinations done at our facility was retrospectively collected in the month of May 2024. Data, including the volume Computed Tomography Dose Index (CTDIvol) value, dose-length product (DLP) value, scan range and the head diameter of the patient measured in the Antero-posterior (AP) and Lateral (LAT) orientations, were documented in a standardized format for analysis. The effective dosage E was then calculated. The mean ± S.D of E for brain CT was 2.5 ± 0.5 mSv. The mean ± S.D for the Effective Diameter DEFF was documented as 159.9 ± 8.7. The correlation (R2) between the E and DEFF showed 0.3315 as its values, indicating a positive correlation. The radiation increases according to the increase in head diameter. This study demonstrates that radiation exposures from CT brain scans may rely on the size of the head. Consequently, additional safety protocols should be implemented for the type of examination so as to reduce the potential risks linked to CT scans.