Investigation of New Refrigerant Blends as R410A Alternatives for Air-cooled Split Air Conditioner
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijpce.3.1.2634Keywords:
R410A, R455A, R466A, R470A, air-cooled split air conditionerAbstract
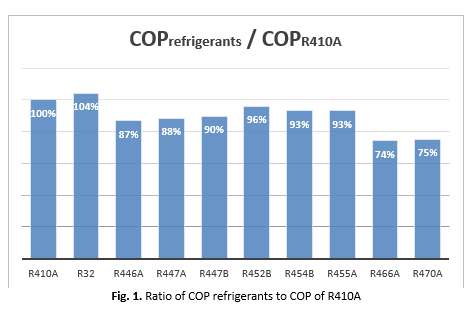
The Kigali Amendment is an international agreement addressing the environmental impact of high-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants and reducing their contribution to climate change. High-GWP refrigerants are potent greenhouse gases that tightly trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, resulting in an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming. The amendment contributes significantly to advancing sustainable practices in the refrigeration and air conditioning industries by limiting the use of these potent greenhouse gases and encouraging the adoption of more environmentally friendly alternatives. As a result, the replacement refrigerants in this study must have lower GWP values than R410A, which aligns with the Kigali Amendment's goals. This study aimed to identify potential refrigerants to replace R410A in air-cooled split air conditioners while adhering to the Kigali Amendment's GWP requirements. By combining environmental indexes and thermodynamic properties, the study can evaluate and compare various refrigerant blends to identify those that are environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and meet the Kigali Amendment's GWP requirement. The evaluation identifies promising R410A replacements, such as R446A for high-temperature applications and R32 for higher-temperature air conditioning. R447B, R452B, and R454B exhibit improved system performance and efficiency due to the slightest temperature glide during phase transition. R454B has the highest Coefficient of Performance (COP) and volumetric refrigeration capacity, indicating greater energy efficiency and a lower environmental footprint. These findings help select appropriate refrigerant alternatives, address environmental concerns, and adhere to Kigali Amendment regulations. This research promotes environmentally friendly refrigeration solutions and sustainable practices in the air conditioning industry.