Experimental and Finite Element Analysis of Multi Layers Composite Materials for Wind Turbine Blade under Aerodynamic Loads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijmr.4.1.1029Keywords:
Experimental, finite element analysis, composite materials, ANSYS, aerodynamic, wind turbine bladeAbstract
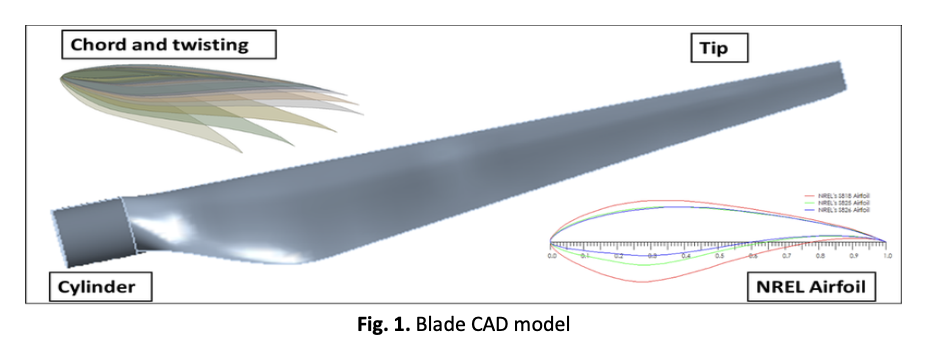
Wind energy is an essential source of sustainable and renewable energy. This paper discussed the strain, stress and deformation procedure involving a small lab-scale wind turbine rotor. In this paper, using a 1.5 MW scale wind turbine as the prototype, the study included selecting an NREL S818-S825-S826 airfoil for General Electric (GE) horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT) and determining the material properties of composite materials with different layers of glass fibres. The laboratory experiment and the ANSYS program were conducted to perform a structural analysis of the blade at various wind speeds with different composite materials to calculate the strain, stress and deformation values in the laboratory and compare them with the ANSYS. The simulation analysis considered two independent variables: wind speed (5, 10, 12, 15, 17 m/s) and different composite materials (virgin, one, two and three layers from fiberglass). The result is improved blade design for strain, stresses and deformation. The results showed good agreement between the experimental and the ANSYS simulation.