Influence of Stenosis Geometry on Magnetohydrodynamic Hybrid Nanofluid Blood Flow and Heat Transfer in Bifurcated Artery
Keywords:
Stenosis, magnetohydrodynamic, hybrid nanofluid, heat transfer, bifurcated arteryAbstract
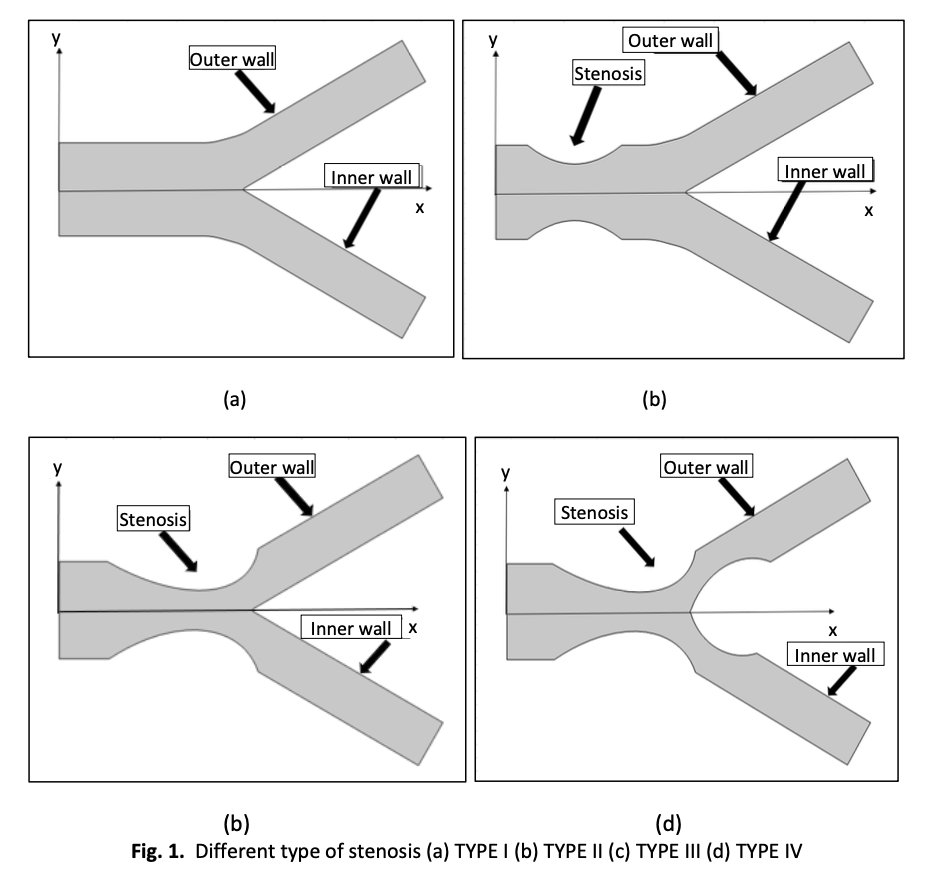
Atherosclerosis, caused by plaque-induced arterial stenosis, restricts blood flow and reduces oxygen delivery to tissues. This study investigates magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) hybrid nanofluid blood flow in bifurcated arteries with different types of stenoses under a uniform magnetic field. A mathematical model is developed for incompressible, laminar, Newtonian flow, with silver (Ag) and gold (Au) nanoparticles dispersed in blood to form the hybrid nanofluid. Simulations are performed using COMSOL Multiphysics and validated against existing literature. Velocity fields and streamline patterns are analyzed to evaluate the effects of stenosis geometry and location on hemodynamics. Results show that incorporating gold and silver nanoparticles improves flow uniformity, while an external magnetic field further enhances performance. The findings indicate that MHD-assisted hybrid nanofluids, combined with optimized stenosis management, present a promising approach for biomedical applications in mitigating the adverse effects of arterial stenosis.