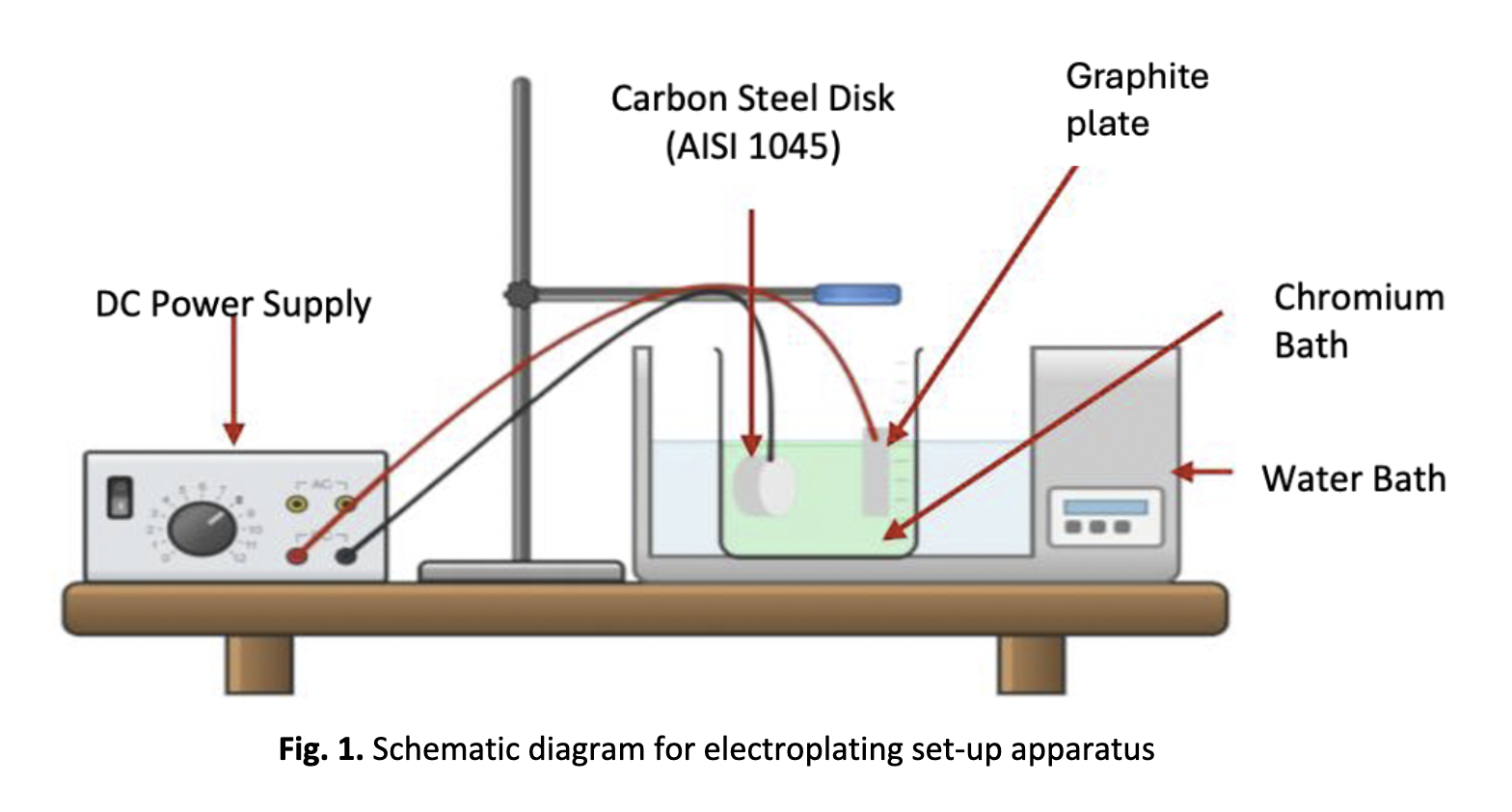
Properties Trivalent Chromium Coating Influenced by Surface Activation Pretreatment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijmpe.1.1.3343aKeywords:
Trivalent chromium, activation, electrodeposition, coatingAbstract
This study presents a novel approach of optimizing trivalent chromium coating development to achieve enhanced properties, focusing on the interplay between surface activation and coating adhesion. Chromium coating aggrandized their application to aircraft, automobile, and machinery industries. However, their application is impeded by insufficient coating adhesion strength. To enhance coating adhesion strength between metal coating and substrate, a surface activation before electroplating is proposed. Advanced characterization techniques, including Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and surface topography testing were employed to investigate the surface morphology, and roughness of the coating. The key innovation lies in correlating these parameters to achieve coating with compact and uniform morphology, resulting in exceptional performance. The activation was done by acid dipping using different types of acid Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl) at different concentrations and dipping duration. The trivalent chromium coating has been deposited at 25A/dm2 for 10 minutes. The study identifies optimal surface activation by utilizing HCl with a concentration of 30 vol% dipped for 120 seconds to achieve superior coating adhesion. These findings significantly advance the understanding of trivalent chromium coating processes and their potential applications in industries demanding high durability. In addition, it was confirmed that a coating layer of trivalent chromium was successfully deposited by electroplating with a thickness more than 5mm with the addition of the activation method. It is concluded that a meticulously developed activation pretreatment procedure is essential before the electroplating process to create a high-quality coating with notable coating protection.