Water Security using Internet of Things (IoT) for Campus Community
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijml.6.1.110Keywords:
Water security, IoT, water quality monitoring, green campusAbstract
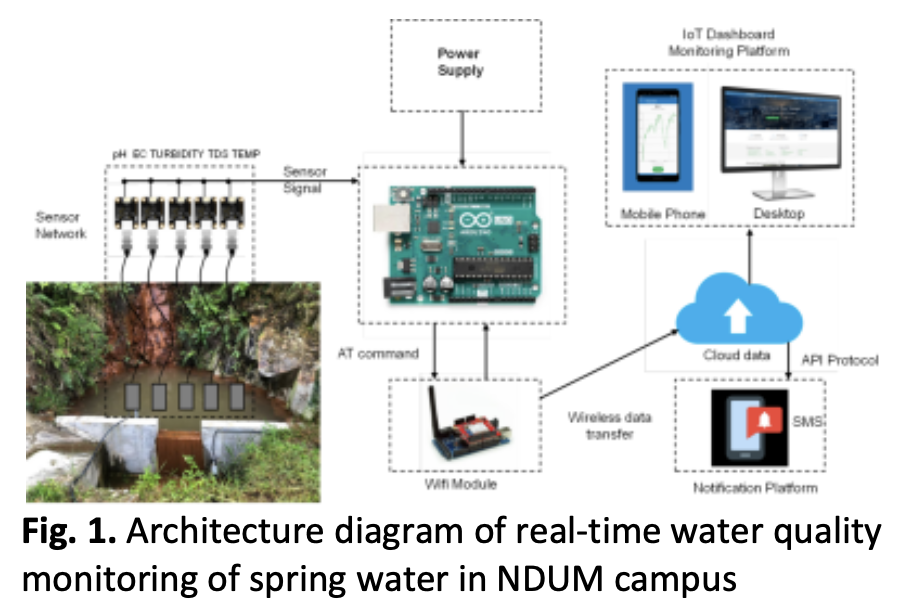
This study addresses the critical need for an integrated approach to monitor the quality of spring water in NDUM campus, combining the precision of conventional in-situ instruments with the real-time systems based on Internet of Things (IoT) technology. The study assesses the spring water quality parameters including temperature, turbidity, pH, TDS, and electrical conductivity. The datasets were analyzed using statistical methods, to identify patterns and relationships. The findings demonstrate a strong correlation between real-time and conventional procedures, confirming the effectiveness of both approaches in accurately assessing the quality of spring water. The outcome from this study may contribute to the propose of a new way of monitoring water quality on campus by using a real-time system. In addition, the outcome also provides baseline information about water quality for the welfare of society and supports the green campus campaign, which may also help in future water security, research, and sustainable water management strategies for NDUM campus area.