Internal and External Barriers to Circular Economy Adoption among Food SMEs in Johor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijeebd.4.1.1324Keywords:
Circular economy adoption, internal barriers, external barriers, JohorAbstract
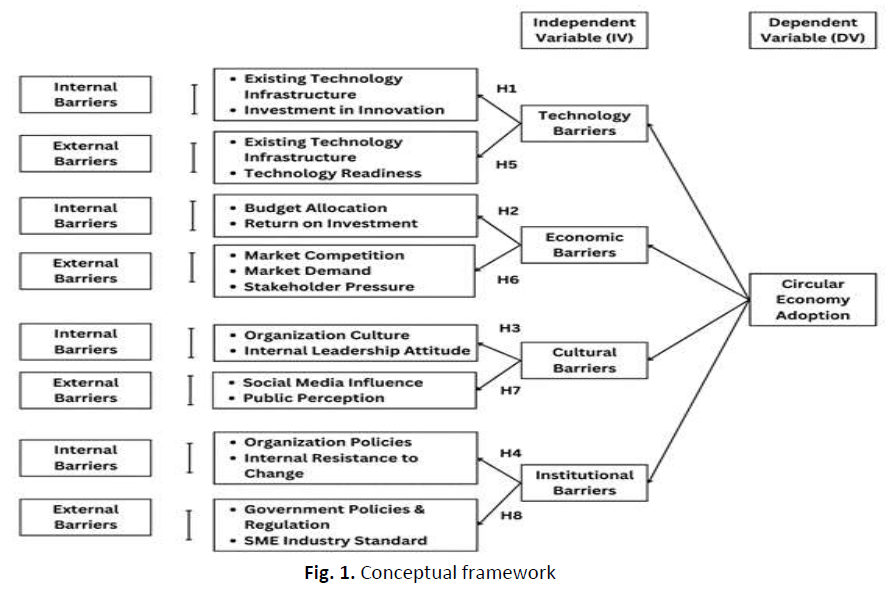
The adoption of the circular economy has grown rapidly, and the owners of food SMEs represent a significant market segment with unique characteristics and preferences. This paper aims to examine both the internal and external barriers to circular economy adoption among food SMEs in Johor. A quantitative research approach and convenience sampling method were used to collect data. The data were gathered through an online survey questionnaire targeting food SME owners in Johor Bahru who were aged 21 and above and had experience with the circular economy. A total of 163 responses were collected and analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS). The findings revealed that the current level of circular economy adoption among food SMEs in Johor Bahru is high. Furthermore, the results indicated that circular economy adoption significantly influences food SMEs both internal and external barriers. Among the barriers, economic factors were identified as the most significant, followed by cultural, technological, and institutional barriers. These findings provide valuable insights for businesses and policymakers, enabling them to better address the needs and preferences of this important consumer segment and enhance their experience with the circular economy.