The Spatial Analysis for Poverty in Malaysia Using the GWR and the PSDM GWR Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijeebd.3.1.1228aKeywords:
Ordinary Least Square (OLS) model, the Parameter-Specific Distance (PSDM) models, Geographical Weighted Regression (GWR), COVID-19Abstract
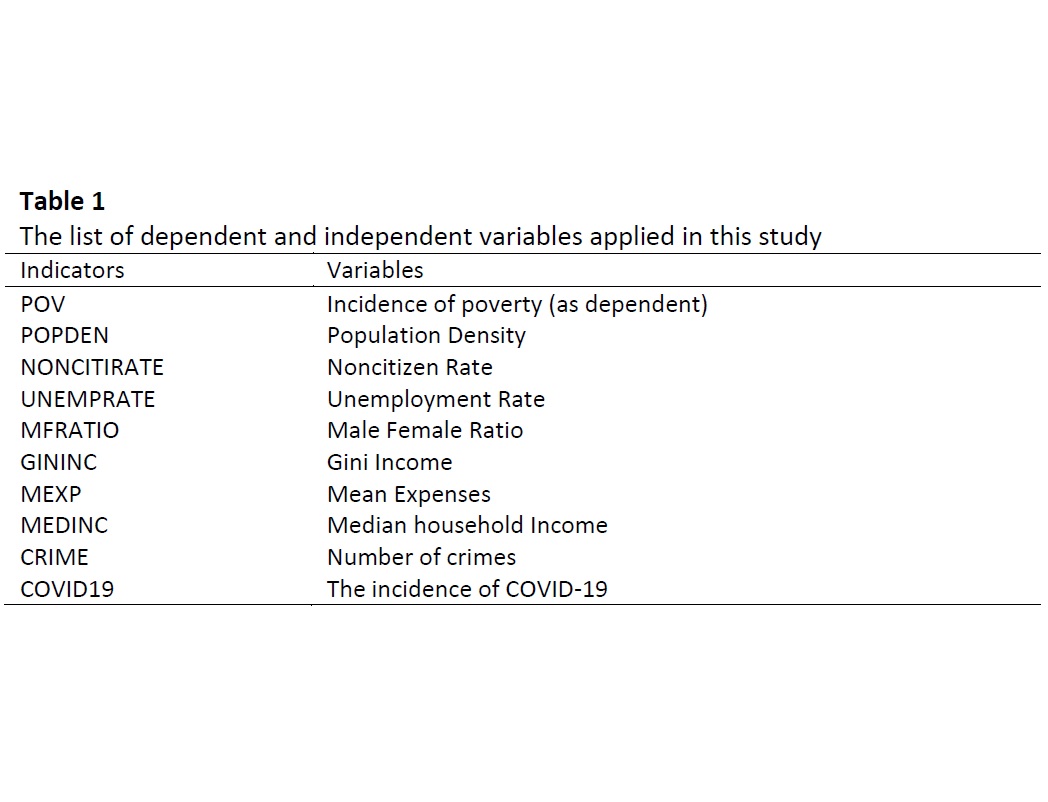
This research examines poverty inequalities from every angle, including their origins, effects on people and communities, and possible governmental responses to the problem. The population density, unemployment rate, non-citizen rate, median income, Gini income, mean expenses, crime rate, and COVID-19 incidence rate were among the factors that were included in this study. The parameter-specific distance (PSDM) models outperform the conventional geographical weighted regression (GWR) models using a multi-dimensional spatial methodology. The new PSDM model's findings indicate that poverty was significantly affected by median household income both before and after the pandemic. Poverty was found to be impacted by both the unemployment rate and Gini income after the pandemic. Furthermore, this research yields distinct relevant elements for each district. The spatial inference guidelines would give policymakers improved direction on the spatial analysis process by improving their comprehension of collinearity and type 1 error. Additionally, statistical inference approaches with integrated spatial modifications were used to analyze relevant variables. According to projections for 2024, Sabah districts were found to have a high prevalence of poverty, which calls for the government to take proactive measures by launching programs in the affected districts.