Sustainable Affordable Housing: Global Trends, Policy Gaps, and Game Changing Practice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijdbes.2.1.118Keywords:
Housing, sustainable affordable housing, technology, green building, policyAbstract
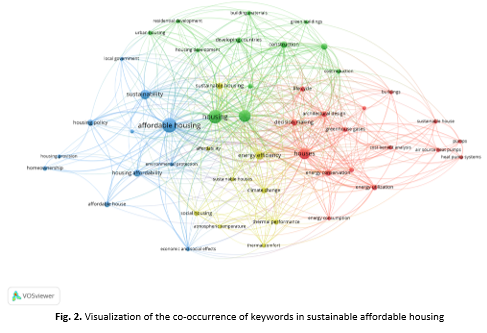
The global housing crisis is increasingly compounded by the need for sustainability, yet balancing affordability with environmental responsibility remains a significant challenge. Many affordable housing projects fail to integrate sustainable practices due to cost concerns, leading to long-term inefficiencies and negative environmental impacts. This study aims to explore trends, efficiency, and policy gaps in sustainable affordable housing through a comprehensive analysis of global practices. The objectives are threefold: (1) to identify key trends in sustainable affordable housing policy, (2) to evaluate the efficiency of current practices, and (3) to identify policy gaps and highlight best practices for future development. Utilizing a mixed-methods approach, this study employs bibliometric analysis to map influential research, a systematic literature review (SLR) to critically assess the existing body of knowledge, and document analysis to evaluate policy frameworks and real-world implementations. Finding reveals three critical themes in the field namely energy and construction cost efficiency, financial accessibility, and sustainable house design. Innovative approaches such as modular construction, smart energy management system, and the integration of renewable energy technologies are improving sustainable affordable housing. This study also finds the significant gaps particularly in policy integration, financial mechanisms, and scalability. Recommendations for future development include stronger green building regulations, targeted financial incentives for sustainable materials, and community-centered approaches to ensure long term affordability and inclusivity.