Innovative Zn-Doped TiO₂ Catalysts for Adsorptive–Photocatalytic Removal of Polyethylene Microplastics
Keywords:
Polyethylene microplastics, Zn-doped TiO₂, microwave-assisted synthesis, visible light photocatalysis, adsorption–photocatalysis, environmental remediationAbstract
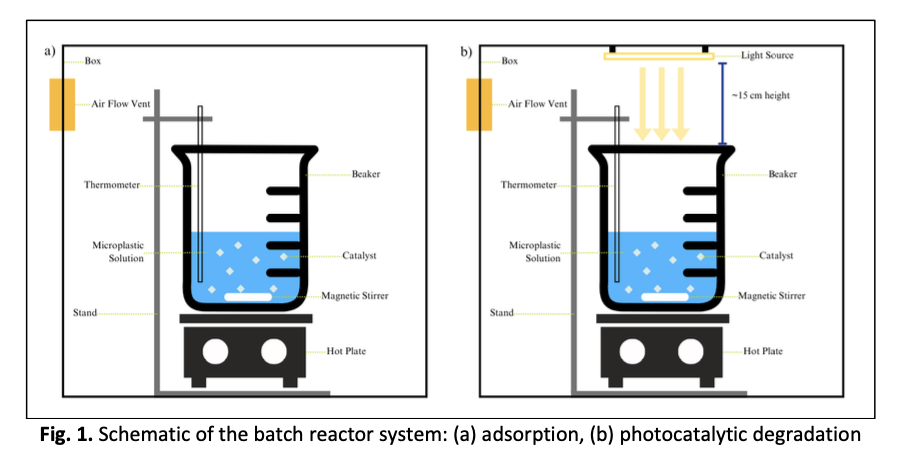
Polyethylene (PE) microplastics persist in aquatic systems, posing ecological and health concerns due to their high resistance to natural degradation. This work explores the application of microwave-assisted zinc-doped titanium dioxide (Zn–TiO₂) catalysts for the combined adsorption and photocatalytic removal of PE microplastics under visible light. Catalysts were synthesized through microwave modification and assessed across different pH levels, catalyst dosages, and initial PE concentrations. The highest photocatalytic efficiency (85%) was obtained under acidic conditions (pH 3) at an optimal dosage of 3 g/L with 10 mg/L of PE. Zn–TiO₂ exhibited superior performance compared to pristine TiO₂ and ZnO, demonstrating enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic activity attributed to the synergistic effect of Zn incorporation, which improved light utilization and reduced electron–hole recombination. Reusability tests confirmed good stability, with 70% efficiency retained after five cycles. These findings establish microwave-modified Zn–TiO₂ as a promising, durable, and sustainable photocatalyst for mitigating microplastic pollution in aqueous environments.