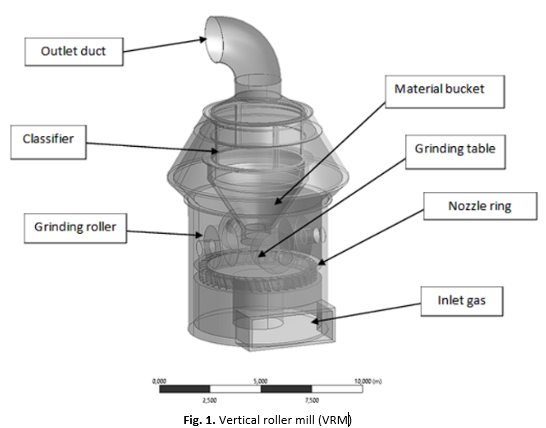
Integration of Air Splitters and Air Deflectors in Vertical Roller Mills: A Computational Fluid Dynamic–Discrete Particle Method Approach to Improve Milling Performance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijcpe.4.1.3345Keywords:
Discrete phase model, particle tracking efficiency, multiphase flowAbstract
This study examines the efficiency of particle tracking using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) in multiphase flow simulations by comparing three configuration scenarios: serial mode (without parallel), parallel mode with default loop-factor settings, and parallel mode with reduced loop-factor. A total of 22,118 particles were tracked in each scenario to evaluate the number of particles that completed their trajectories (escape), those that did not complete (incomplete), and those trapped in parallel loops (incomplete_parallel). Efficiency was calculated using the ratio of escape particles to the total number of particles tracked. The results showed that the parallel scenario with the default loop factor had the highest efficiency rate, approximately 62%, where most particles successfully left the simulation domain. In contrast, the serial mode only showed an efficiency of around 35%, indicating that many particles failed to complete their trajectories due to iteration limitations.