Enhancement of Cholesterol Oxidase Production by Rhodococcus UCC0018 via Optimization of Fermentation Conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijpce.3.1.110Keywords:
Cholesterol oxidase, Rhodococcus sp., fermentation, optimizationAbstract
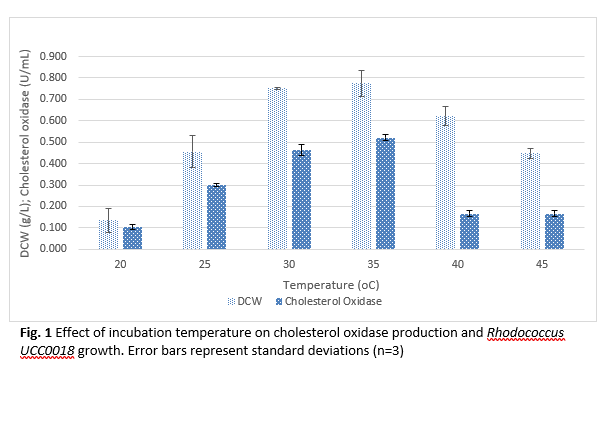
Cholesterol oxidase is an important enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of cholesterol to cholest-4-en-3-one, with the simultaneous reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. It has gained significant attention due to its wide range of applications in medical diagnostics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. Cholesterol oxidase is crucial in reducing cholesterol levels by breaking it into less harmful byproducts, making it a valuable tool in managing cholesterol-related health issues. The enzyme is primarily produced through microbial fermentation using microorganisms. However, the yield and efficiency of cholesterol oxidase production are highly dependent on fermentation conditions, including temperature, pH, and agitation rate, which significantly influence microbial growth, enzyme stability, and overall productivity. The initial production of cholesterol oxidase and cell growth under non-optimized conditions revealed suboptimal performance, with enzyme activity and cell dry weight (DCW) peaking at lower levels.