Bioinformatics and Experimental Analysis of miR-21-5p-Mediated Gene Regulation in Moringa-Supplemented Mice
Keywords:
miR-21, miR-21-5p, Moringa oleifera, gene regulationAbstract
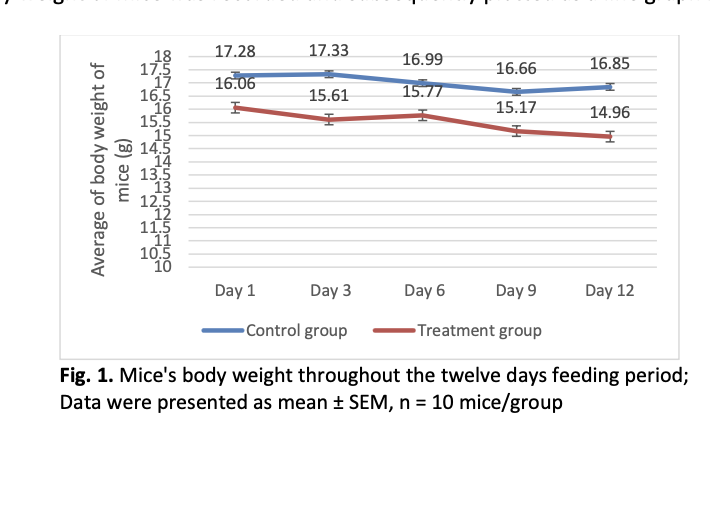
Modulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) through miRNA-based therapeutics faces several challenges, including in vivo instability and activation of the innate immune response. Moringa oleifera offers a promising natural alternative for regulating miR-21-5p expression due to its rich phytochemical profile and lower immunogenic risk. This study investigated the impact of Moringa extract on miR-21-5p expression in BALB/c mice, followed by bioinformatic prediction and analysis of the downstream effects on its identified target gene. Mice were split into two groups, with the treatment group receiving 300 mg/kg of Moringa extract via oral gavage for 12 days in a row, while the control group was given the same amount of distilled water. Gene expression levels were analysed using RT-PCR. Bioinformatic analysis using TargetScan predicted a total of 303 potential miR-21-5p’s target genes, among which SMAD7 was chosen for further RT-PCR analysis due to its strong predicted interaction and known role in disease regulation. The results showed that the treatment group's expression of miR-21-5p was significantly downregulated (p = 0.028), with the average normalised band intensity decreasing from 0.55 ± 0.059 in the control group to 0.21 ± 0.009 in the treatment group (n = 3 mice per group). This reduction was accompanied by an increase in SMAD7 mRNA levels, from 2.61 ± 0.979 to 3.29 ± 1.374 (p = 0.7083), indicating that miR-21-5p directly targets SMAD7. Consequently, the potential of Moringa extract as a natural modulator of miRNA expression is supported by these findings.