Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Bloom with Prey-Predator Interaction
Keywords:
Harmful algal blooms (HABs), phytoplankton, prey-predator, stabilityAbstract
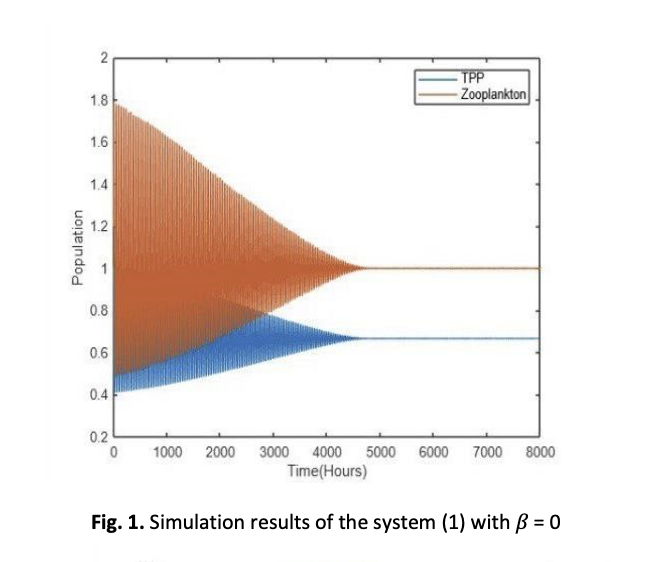
An algal bloom is a condition by extensive algal growth in a specific area that is consider harmful when the bloom causes a damaging effect. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) events are dangerous to human, ecosystem, and marine creatures. Therefore, this study is proposed an extension of the HABs mathematical modelling to describe the HABs events. This model consists of two variables: Toxic-Producing Phytoplankton (TPP) population and zooplankton (Z) population. This research considered the prey-refuge factor to evaluate its stabilizing and destabilizing impacts on the system. Stability analysis is conducted to determine the stability condition of the model and the result is verified by applying the numerical simulations. Numerical simulation was performed across varying refuge prey levels to observe system behaviors. A model of prey-predator interaction is being studied to show the effect of HAB. The result show that the low prey refuge enhances stability and balanced species coexistence while higher refuge prey rate reduce zooplankton predation effectiveness will lead to unstable dynamic and increases HAB risk. This model provides a theoretical basis for predicting blooms occurrence and contribute to the development of early warning strategies for HAB management.