Improvement of Geotechnical Properties of Kaolin Clay using a combination of Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA), Eggshell Waste, Guar Gum: A Preliminary Study
Keywords:
Clay soil, Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA), Eggshell Powder (ESP), Calcined Eggshell (CES), Guar Gum (GG), soil stabiliser, unconfined compressive strengh (UCS)Abstract
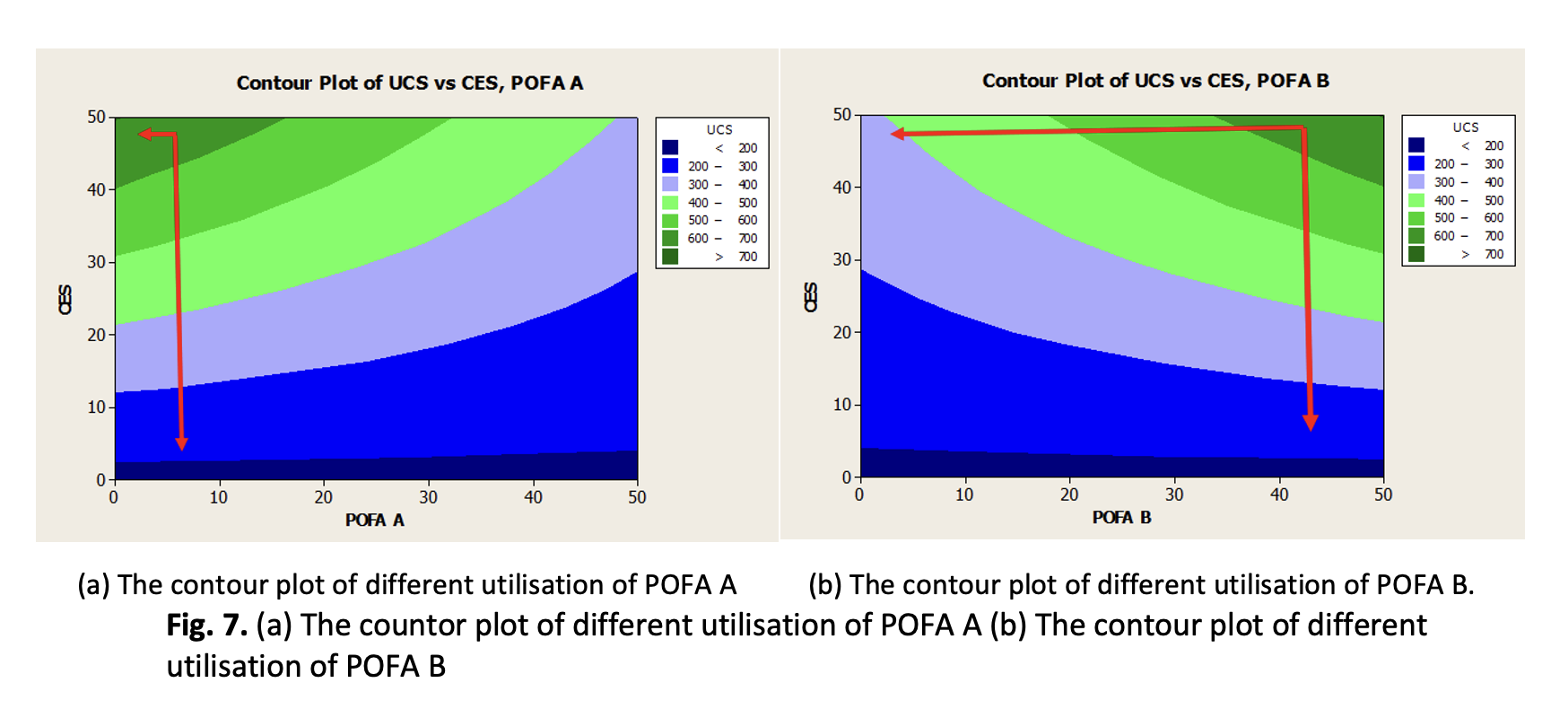
Clay soils with high plasticity and water content pose significant challenges in construction due to their low bearing capacity, settlement issues, and instability. Traditional soil stabilisers such as cement and lime improve these properties but involve challenges due to environmental concerns, resource depletion, and their performance limitations in some soil types. This study explores the potential of using sustainable and alternative soil stabilisers derived from agricultural and industrial wastes, specifically Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA), Eggshell Powder (ESP), Calcined Eggshell (CES), and the natural additive Guar Gum, to enhance the geotechnical properties of problematic soils. The research investigates the effects by formulating three binder combinations: POFA with ESP, POFA with CES, and POFA with CES plus Guar Gum, on the strength development, curing time, and dosage efficiency in stabilising Kaolin Clay. These formulations were tested on Kaolin Clay to evaluate their impact on unconfined compressive strength (UCS) across various dosages and curing periods. Results indicate that the combination of POFA and CES achieved superior strength enhancement compared to the other formulations, with UCS values significantly higher than untreated soils. The addition of Guar Gum did not improve the strength but influenced the binder’s behaviour. Optimal performance was observed at a binder dosage of 30% with a curing period of 7 days. This study concludes that POFA and CES can serve as effective, eco-friendly soil stabilisers that reduce dependency on conventional cement and lime. Their use supports sustainable construction practices by utilising local waste materials and improving soil stability for infrastructure development. The findings recommend the practical application of POFA and CES mixtures as viable alternatives for road subgrades and other geotechnical works.