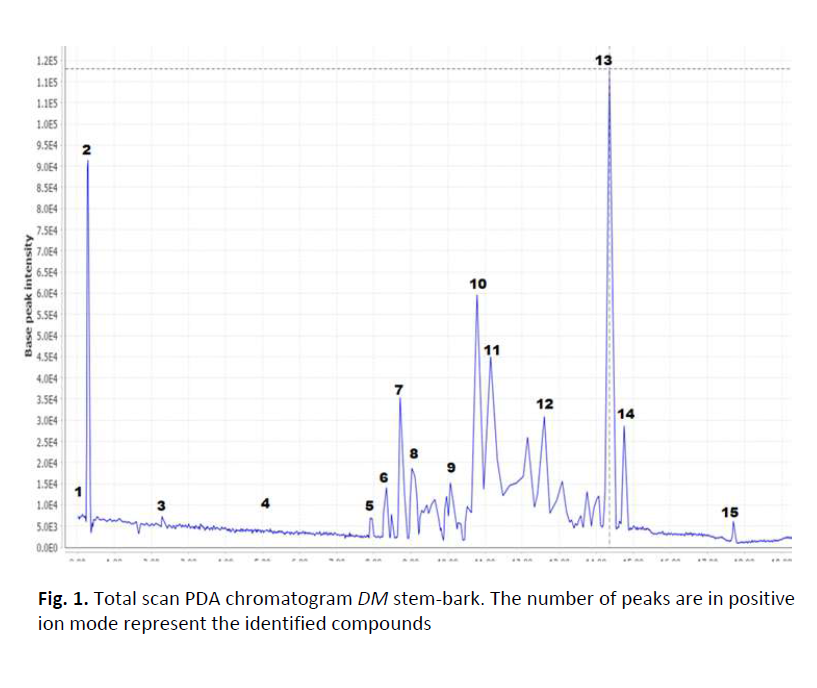
Metabolite Profile, Antioxidant Activity and Ameliorative Efficacy of Diospyros Mespiliformis on Carbon Tetrachloride (CCL4) Induced Oxidative-Stress in Albino Mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/scbtrj.4.1.4167bKeywords:
Antioxidant activity, Diospyros mespiliformis, albino mice, phytochemicals, metaboliteAbstract
Liver diseases are deadly and requires continuous medication, conventional treatment is harmful and expensive, so there need for hepatoprotective remedy from plant sources. Bioactive phytochemicals were profiled and the efficacy of Diospyros mespiliformis (DM) stem-bark extracts was evaluated against carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) induced oxidative stress in mice. Diospyros mesopiliformis have been reported for various activities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiiflammatory. Based on the previous reports it was anticipated D. mesopiliformis will ameliorate CCL4 induced liver damage in murine model. Metabolite profile of the extract was obtained using LC-MS/MS. Liver marker enzymes and oxidative stress biomarkers in serum and liver tissue were assessed. Liver tissues and homogenates were assessed for histopathology and estimation of MDA, catalase, superoxide dismutase, and Glutathione S-Transferase activities, qRTPCR mRNA expression of hepatic tissue Glutathione S- Transferase was performed. Free radical scavenging activity of the extract were assessed using DPPH quenching assay, FRAP and peroxide test. In-silico molecular modelling was also conducted. Alkaloids, amino acids, anthraquinone, nucleoside derivative, phenolic acid derivatives, fatty amide, flavonoid, and vitamin B12 were detected The CCL4 caused drastic weight loss in mice, induced liver damage through elevated marker enzymes and bilirubin, reduction in total protein and albumin as well as significant decrease in tissue catalase, GST and superoxide dismutase activities and also marked increase in serum MDA level. Glutathione-S transferase mRNA expression of hepatic tissue and histopathological results also supported the biochemical findings. Extract exhibited concentration dependent free radical scavenging activity. Molecular modelling data corroborates that some of the bioactive compounds may possess the potential to enhance the activities of the antioxidant enzymes. Conclusion: The DMstem-bark extract was beneficial in modulating the alterations induced in liver and serum variables of mice under the effect of CCL4.