Design of CMOS-based Instrumentation Amplifier for Energy Harvesting in Biomedical Application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/scbtrj.4.1.2840bKeywords:
Electrospinning, PET, fiber, NaOH surface treatment, fibrin gel, coatingsAbstract
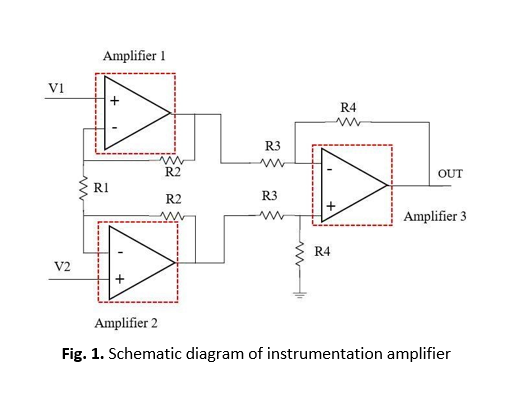
Biomedical signals usually are very weak due to low amplitude. An instrumentation amplifier which practically applied in biomedical applications is designed due to its numerous advantages such as gain can be adjusted easily by a single control without changing the whole structure and its common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) is high. This project proposed a three op-amp instrumentation amplifier by using three two-stage complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) operational amplifier and designed with 130 nm CMOS technology. The gain of the proposed amplifier for pre-layout simulation is 64.15 dB with input-referred noise of 10.41 µ(V/√Hz) and power dissipation of 115.6 µW and a CMRR of 107.25 dB. The gain of the amplifier for post-layout simulation is 63.69 dB with input-referred noise of 10.52 µ(V/√Hz), the power dissipation of 115.6µ W, and CMRR of 100.39 dB. Apart from that, the amplifier is designed with a size layout of 5.25 µm x 104 µm. The circuit designed will be useful to embed together in energy harvesting system for wearable biomedical system.