Human Milk Immunity and Breastfeeding among Lactating Individuals with COVID-19: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/scbtrj.4.1.117bKeywords:
COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, breastfeeding, human milk, breast milkAbstract
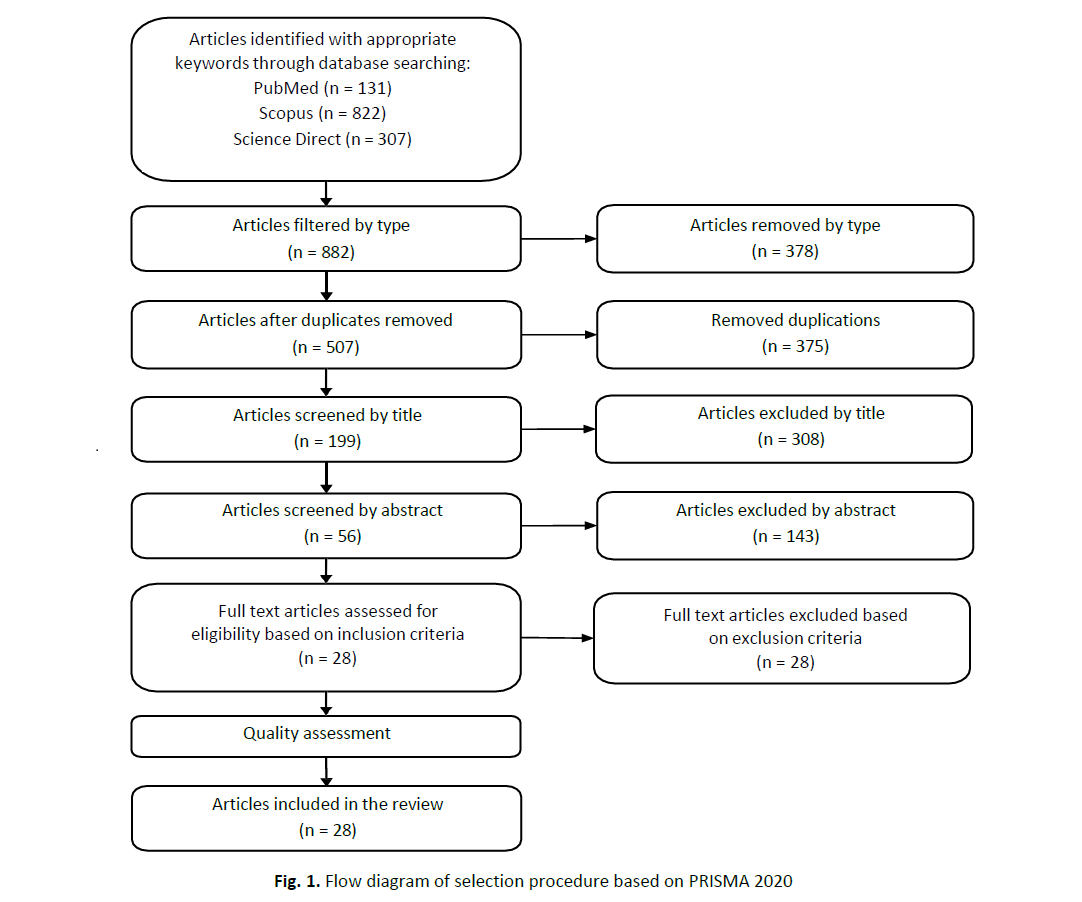
Safety of infants nursed by their infected mothers is crucial to knowing whether the virus can be transmitted vertically through mothers’ milk. This study aims to collect and compile data from available studies on the immunological and microbiological components that can be found in COVID-19 infected mothers who breastfed their infants and to investigate the state of the infants who received breast milk while their mother is still confirmed to be positive with the virus. A systematic review was done from 28 articles that have passed the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study. Qualitative data synthesis was applied to extract and analyze the results. Breast milk of mothers who were still infected with the virus does not harm the infants and instead giving them the extra protection against them. The contents in the mother’s milk also were found to have neutralizing ability against the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and able to inhibit neutralizing antibodies (NAb) against receptor-binding domain (RBD) protein mutants. Infants who were infected with COVID-19 did not obtain the virus from their mother’s milk and no further complications were found in the infants after they were healed from the virus. Mothers can be well assured to continue breastfeeding their infants while contracting the disease as there is no evidence of virus transmitted through breast milk found. Appropriate strategies and guidelines must be followed during the breastfeeding process to minimize the risk of transferring the virus to infants through other method such as coughing or sneezing.